oPools™ Oligo Pools
Start with solid bases
Use oPools Oligo Pools for accurate, reliable, and affordable CRISPR libraries; primer pools for multiplex PCR; gene construction; data storage; and FISH analysis. These pools of custom single-stranded DNA sequences offer high fidelity, uniformity, low error rates, and low dropout rates. This means that you can avoid amplification bias, varying concentrations, or high error rates that are often encountered when using pooled oligos from other suppliers.
Ordering
oPools Oligo Pools
Pooled DNA oligos delivered dry in a single tube.
Available in convenient sizes:
| Scale (pmol/oligo) | Number of oligos per pool | Oligo length (bases) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 100 to 20,000 | 40 to 350 |
| 10 | 10 to 2000 | 40 to 350 |
| 50 | 2 to 384 | 40 to 350 |
* Regardless of pool size, the first 3300 bases will be charged at the oPools DNA Base 1 rate. Bases 3301–50,000 will be charged at the oPools DNA Base 2 rate, bases 50,001–100,000 will be charged at the oPools DNA Base 3, and bases more than 100,000 will be charged at the oPools Base 4 rate.
Product details
oPools Oligo Pools are single-stranded DNA sequences that are used for CRISPR library construction, primer pools for multiplex PCR, gene construction, data storage, and FISH analysis.
Proprietary DNA synthesis equipment permits rapid, high-quality synthesis of nucleic acids. This platform is the same proprietary synthesis platform used to make IDT Ultramer™ DNA Oligos. It uses an "extra rich" synthesis cycle for long oligos. Along with this refined synthesis cycle, oPools DNA Oligos use a unique solid support specifically optimized to synthesize high-quality oligos up to 350 bases in length.
Specifications
| Standard processing | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Length | 40–350 bases/oligo | ||||||
| Scale (number of oligos) |
| ||||||
| Mixed bases | N = A, C, G, and T K = G and T • Limited to 10 mixed bases per oligo | ||||||
| Modifications | 5′ phosphorylation | ||||||
| QC and quantification | None | ||||||
| Shipping container | 2 mL tube | ||||||
Shipping and storage
- Shipped dry
- Turnaround time: 4–7 business days from order to delivery
- Short-term storage, up to 6 weeks: room temperature (15 to 25°C) or 4°C
- Long-term storage, up to 24 months: –20°C
Product data
Proprietary DNA synthesis equipment permits rapid, high-quality synthesis of nucleic acids.

Figure 1. IDT proprietary platforms have a better coupling efficiency than other suppliers, which provides more full-length oligonucleotides in your order. Small increases in coupling efficiency (≤1%) result in measurable increases in full-length product yield. The curves represent the theoretical yield for different lengths of oligos based on a coupling efficiency of 99.6% (IDT oligos, n = 34,627) and 99.4% (other supplier, n = 77 from three different suppliers) using the formula, percent full length product = (eff )(n-1)*100 where eff = coupling efficiency (for example, 99.4% = 0.994) and (n–1) is the number of coupling reactions needed to make an oligo of length n.
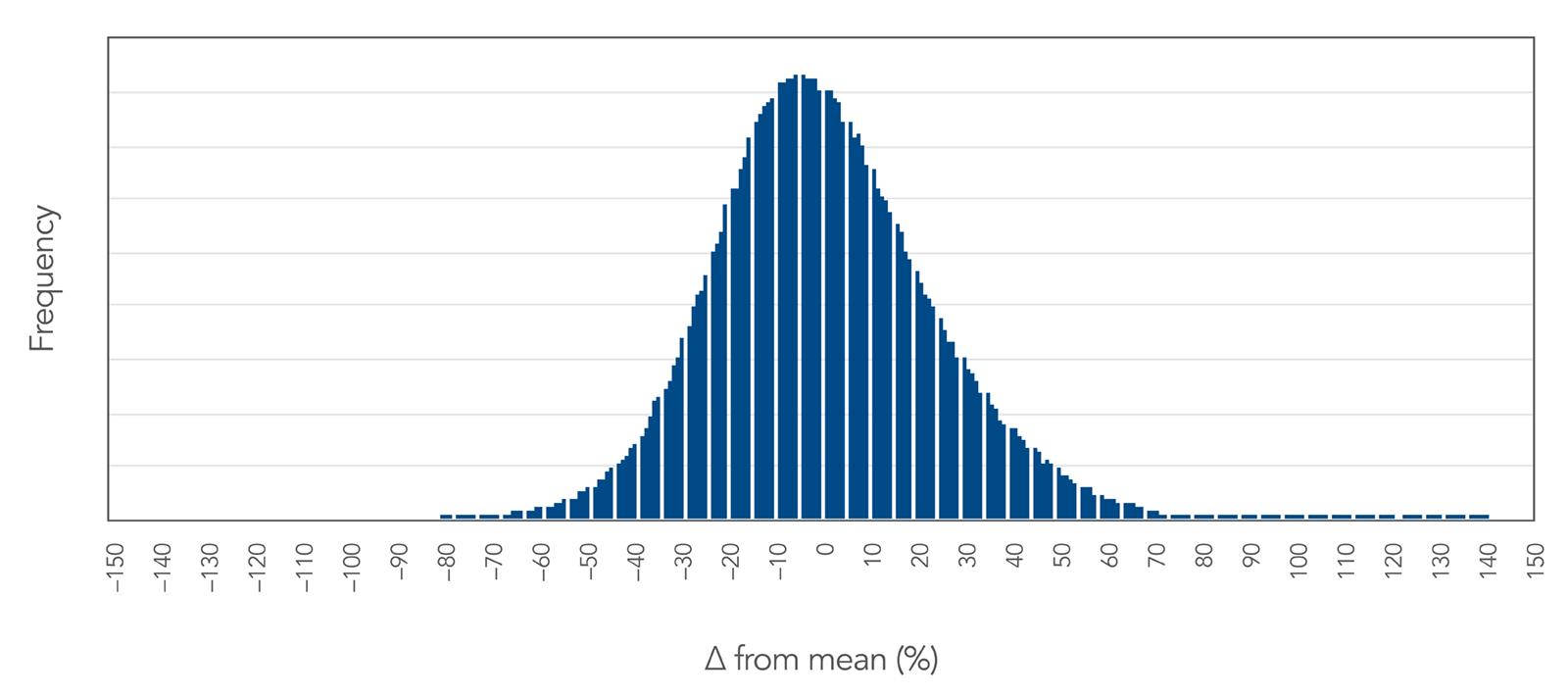
Proprietary DNA synthesis equipment produces an even oligo yield distribution.
Figure 2. Proprietary DNA synthesis results in an even yield distribution of oPools Oligo Pools. This even yield distribution is shown here as a function of % difference from the mean. The standard deviation observed across ½ million sequences is less than 23% of the mean, demonstrating a high level of uniform sequence representation.
oPools Oligo Pools demonstrate low dropout rates
Dropout rate refers to the likelihood that any individual sequence is not present in the final pool. This rate can vary by length and sequence complexity. The average dropout rate for oPools oligos across all length ranges was 0.8% based on a sample size of over 900,000 oligos.
Resources
Frequently asked questions
How do I resuspend my oPools™ Oligo Pools to my desired concentration?
Calculate the appropriate resuspension volume for your oPools product with the IDT Resuspension Calculator.
First, convert the oPool scale—provided in pmol—to a nmol quantity.
If your desired final concentration is µM per oligo, use this equation to determine your quantity:
pmol per oligo / 1000 = # nmol per oligo
Example 1. Final concentration of 1 µM per oligo.
Scenario: 50 pmol oPools Oligo Pool
Quantity: 50 pmol oPools Oligo Pool / 1000 = 0.05 nmol
Final concentration: 1 µM
Resuspension calculator (Figure 1):
- Enter the quantity that you calculated
- Enter your final concentration
- Select Sgl-Stranded DNA (single-stranded DNA)
- Click Calculate

Figure 1. 50 pmol oPools Oligo Pool resuspended to 1 µM per oligo.
If your desired final concentration is nM per oligo, you can convert using this equation:
nM concentration / 1000 = # µM
Example 2. Final concentration of 100 nM per oligo.
Scenario: 50 pmol oPools Oligo Pool
Quantity: 50 pmol oPools Oligo Pool / 1000 = 0.05 nmol
Final concentration in µM: 100 nM / 1000 = 0.1 µM
Resuspension calculator (Figure 2):
- Enter the quantity that you calculated
- Enter your final concentration per oligo that you calculated
- Select Sgl-Stranded DNA (single-stranded DNA)
- Click Calculate

Figure 2. 50 pmol oPools Oligo Pool resuspended to 100 nM per oligo.
If your desired final concentration is per pool, use this equation:
(pmol per oligo x # of oligos in pool) / 1000 = # nmol per pool
Example 3. Final concentration of 1 µM per pool.
Scenario: 50 pmol oPools Oligo Pool containing 100 oligos
Quantity: (50 pmol x 100 oligos) / 1000 = 5 nmol
Final concentration: 1 µM
Resuspension calculator (Figure 3):
- Enter the quantity that you calculated
- Enter your final concentration
- Select Sgl-Stranded DNA (single-stranded DNA)
- Click Calculate

Figure 3. 50 pmol oPools Oligo Pool containing 100 oligos resuspended to 1 µM per pool.
Is each oligo that goes into oPools™ Oligo Pools manufactured individually?
Yes, all oligos that go into oPools Oligo Pools are synthesized separately. The oligos are pooled before shipment.
Are there any purification options available for oPools™ Oligo Pools?
oPools Oligo Pools go through the standard desalting process.
We do not offer additional purification as the manufacturing process is designed to be as efficient as possible.
If oPools™ Oligo Pools are not quantified, how are different yield options offered?
The individual oligos in oPools Oligo Pools are pooled based on an assumed average yield. This average yield was generated using historical data from previously synthesized IDT Ultramer™ oligos.
Are there any quality guarantees on oPools™ Oligo Pools similar to other IDT oligos?
As there are no QC checks performed on oPools Oligo Pools, there are no guarantees in terms of sequence identity or individual oligo purity.
While we expect that the vast majority of sequences ordered in the pool will be present, we cannot guarantee that any individual oligo is present in the pool.
Historical data has shown the percentage of oligos missing from the pool to be less than 1%.
What quality control is done on oPools™ Oligo Pools?
The oPools Oligo Pools manufacturing process is designed to be as efficient as possible.
Therefore, there are no quality control checks or quantification.
What diluent options are available for oPools™ Oligo Pools?
The oPools Oligo Pools manufacturing process is designed to be as efficient as possible. Therefore, we do not offer any formulation services on oPools Oligo Pools. All oPools Oligo Pools are delivered dry.
Why should I consider purification of my oligos?
Purification removes truncated products and other synthesis impurities. Our experience has shown that purifying an oligonucleotide that will be used in demanding applications saves both time and money in the long run. We recommend considering additional purification for any oligonucleotide that will be used for an application other than routine PCR, qPCR, or Sanger DNA sequencing.
As a general rule, IDT also recommends that any oligonucleotide longer than 40 bases should receive further purification. For questions, please contact us.
Why are my oligos a yellow/brown color?
Customers who are new to working with large amounts of material are sometimes surprised when they see a yellow or brown discoloration to their oligos. If you have experienced this, do not worry. Color variation is normal in custom synthesis, especially as concentration increases. Importantly, IDT does not expect this to affect oligo function in our customers' experimental applications.

The image above depicts normal color variation as seen in oligo pools which are formulated to the same concentration (200 nmol oligos in 15 mL solution). In general, modified oligos at larger scales are more likely to display the variation seen above, while small-scale unmodified oligos (e.g., 25 nmol) tend to remain colorless in solution.
What is the difference between scale and yield and why don’t I receive that full amount designated by the scale I order?
Oligo synthesis is accomplished through a series of steps, including coupling of individual bases, cleaving the oligo from the solid support, desalting, and if requested, purification of the oligo by HPLC or PAGE. No chemical reaction occurs with 100% efficiency, and, thus, each of these steps will incur a loss of final yield, which varies from specific sequence synthesis to synthesis.
Due to this variation, IDT custom oligos are ordered according to the amount of starting material used for the synthesis, referred to as the scale. While we cannot predict the actual final yield, we do guarantee a specific minimum yield for each oligo based on its sequence, starting scale, and the typical yield obtained under those specified conditions.
If you would like to know the minimum guaranteed yield for a specific oligo, simply add it to your Shopping Cart. The Shopping Cart provides you with the guaranteed minimum yield. If it is insufficient or excessive for your needs, simply edit the scale.
Please contact us if you have any questions about the yield you have received.
What are the length restrictions for your DNA oligos?
Standard DNA oligos are synthesized up to 100 bases, while our high fidelity Ultramer™ Oligonucleotides can provide single-stranded DNA up to 200 bases.
Beyond 200 bases, we offer our new gBlocks™ Gene Fragments which are double-stranded DNA constructs available from 126 bp up to 2000 bp.
I received my oligo shipment, and it is marked PARTIAL. What does that mean?
Partial shipping means that we are shipping the oligos you ordered to you as they are completed, rather than our default method of waiting to ship until the entire order is complete, with all of the oligos shipping at the same time. We make every effort to synthesize and ship your oligos as quickly as possible because we know that they are time sensitive.
On occasion, one or more oligos may become delayed, e.g., because they did not pass one of our quality control checks or their processing took longer than anticipated. In these cases, we can ship you a partial order at your request. You can also choose to have your order ship partial if you know some of your oligos will take longer than others (because of purification, etc.)—such requests will incur an extra shipping charge.
If you would like to set an order to ship partial, you can request it at the time of checkout or contact us.
How do I determine the Tm of my sequence?
IDT offers a free online calculator, the OligoAnalyzer™ Tool, that will determine the Tm of your oligonucleotide sequence for reaction conditions you specify.
Be sure to include the Mg2+ and dNTP concentrations you plan to use in your reaction, as this will affect the Tm for your oligo.
For what applications is it ok to use standard, unmodified desalted oligos?
Standard desalted oligos can be used in routine PCR, qPCR, and DNA sequencing applications.
Through improvements to the traditional phosphoramidite chemistry and advances in instrumentation, IDT has obtained a coupling efficiency that allows standard desalt oligos to work well for these applications.
Do you do post synthesis sequence analysis of oligos?
The products we perform post-synthesis sequencing on are the double-stranded gBlocks™ Gene Fragments, and the Gene and Mini Gene™ synthetic genes.
Can I anneal my DNA oligos at room temperature and if so, what buffer should I use?
Although it may be possible to anneal oligos at room temperature, heating to denature the oligos and then cooling slowly to anneal the two oligos will help to ensure more efficient annealing and favor the stable duplex formation.
If you choose not to heat the oligos, it would be prudent to carefully screen the oligos for secondary structures which could interfere with the annealing reaction.
More information on how to anneal oligos can be found in the Annealing Oligos DECODED™ article.
Are there deletion products in a standard desalt preparation of an oligo?
Though the majority of product will be the desired sequence, standard desalt oligos will contain a heterogeneous population of sequences, and this heterogeneity will increase with increasing length of the oligo. Oligos are synthesized 3'->5', base by base, through a series of chemical reactions. Chemical reactions are rarely, if ever, 100% efficient; the coupling reaction itself is approximately 99.6% efficient. With each base addition, less than 1% of the growing oligonucleotide chains will not undergo base extension.
After base coupling, we perform a capping step to prevent any truncated molecules from participating in further base addition. Because the capping reaction is slightly less than 100% efficient, a very small percentage of the truncated mutants will remain uncapped and can react during subsequent couplings steps. This leads to the formation of deletion mutants. The resulting oligonucleotide preparation, while comprised mostly of the ordered sequence, is a mixture of the full length oligos, truncated sequences, and sequences with internal deletions.
For exceptionally long oligos, such as our Ultramer™ Oligonucleotides and xGen™ Hyb Panels, IDT uses a proprietary IDT Ultramer synthesis process, which has been designed to give a high coupling efficiency (99.6%). This high coupling rate helps to allow us to synthesize long oligos (xGen Custom Hyb Panels are 60–120 bases long) with a high percentage of full-length product.
What are the ideal storage conditions for promoting long term oligo stability?
For long term oligo storage, temperature is the most important factor to consider. For long term storage, whether oligos are dried down, or resuspended in non-DEPC treated water or TE buffer (10 mM Tris pH 8.0, 0.1 mM EDTA; such as IDTE), we recommend that you store your oligos at –20°C.
For 4°C storage, oligos are stable for at least 60 weeks when stored dry, or resuspended in non-DEPC treated water or TE buffer (10 mM Tris pH 8.0, 0.1 mM EDTA; such as IDTE).
It is also important to note that for DNA oligos, an acidic pH can induce depurination, therefore maintaining a neutral pH is important. For RNA oligos a neutral pH is also important, as basic pH buffers can induce RNA breakdown.
Please see the DECODED, Storing oligos: 7 things you should know, for data on oligonucleotide storage and a more thorough explanation.
Are IDT oligos desalted (salt-free)?
The desalting process does remove the majority of these organic molecules, though trace amounts can still be present in a shipped oligo.
For the most demanding applications sensitive to even trace amounts of salts, e.g., NMR or crystallography, upon receipt we recommend dialyzing your oligos or using a size exclusion column as a clean-up step.
Are IDT oligos DNase and RNase free?
All of the custom DNA and RNA oligonucleotides that IDT offers are synthesized chemically, not enzymatically. As a result, there should not be DNase or RNase present.
It is worth noting that there are abundant nucleases present in most environments, so good laboratory practice is very important to minimize potential exposure. IDT also offers RNaseAlert® and DNaseAlert™ substrates to help identify nuclease degradation.